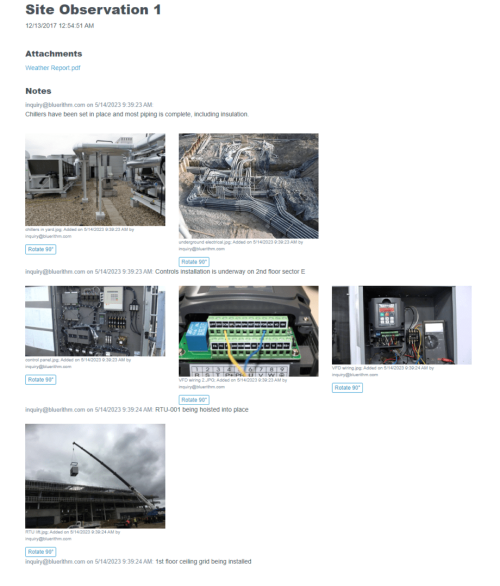
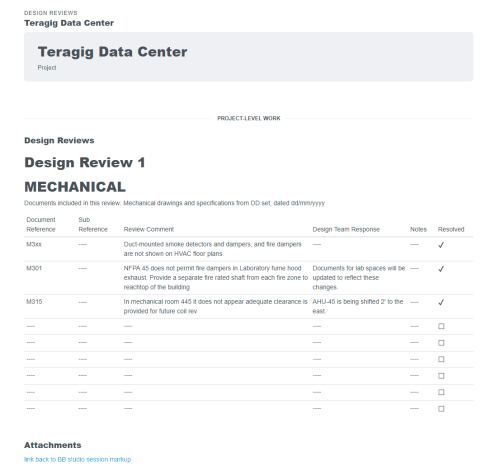
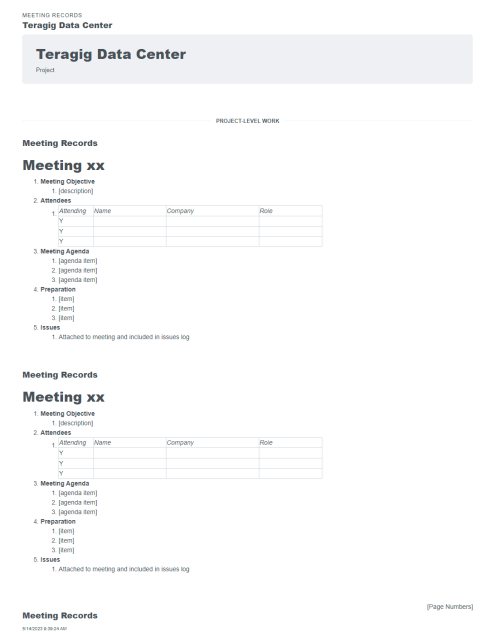
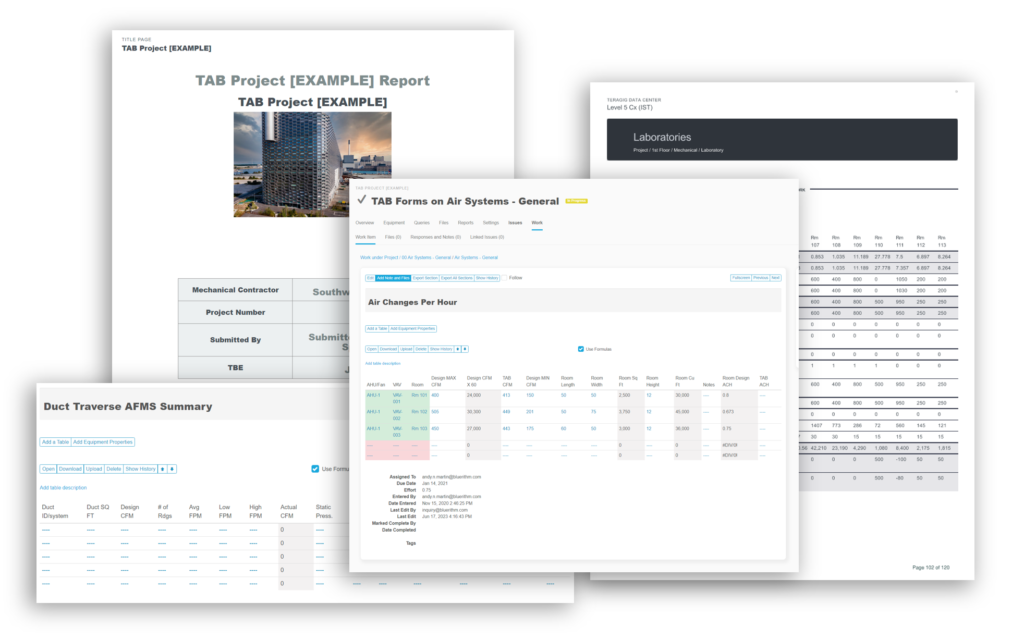
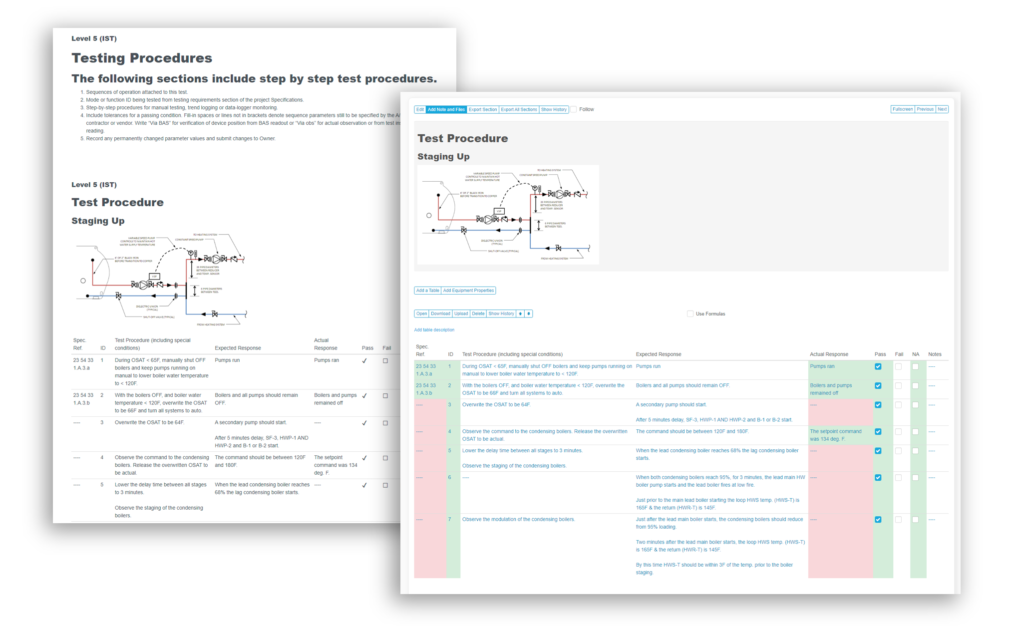
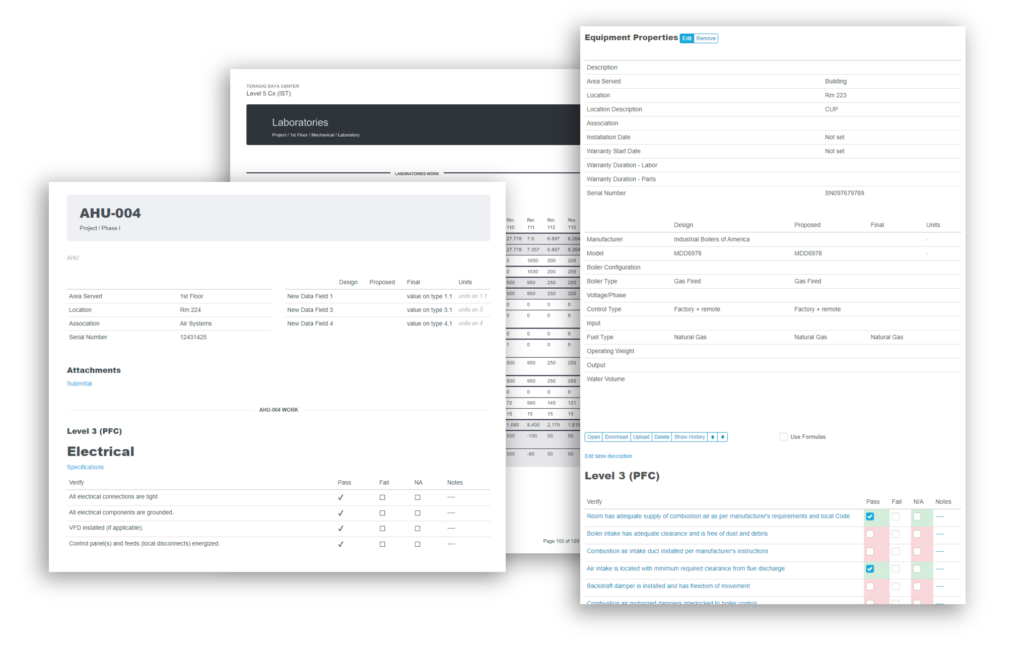
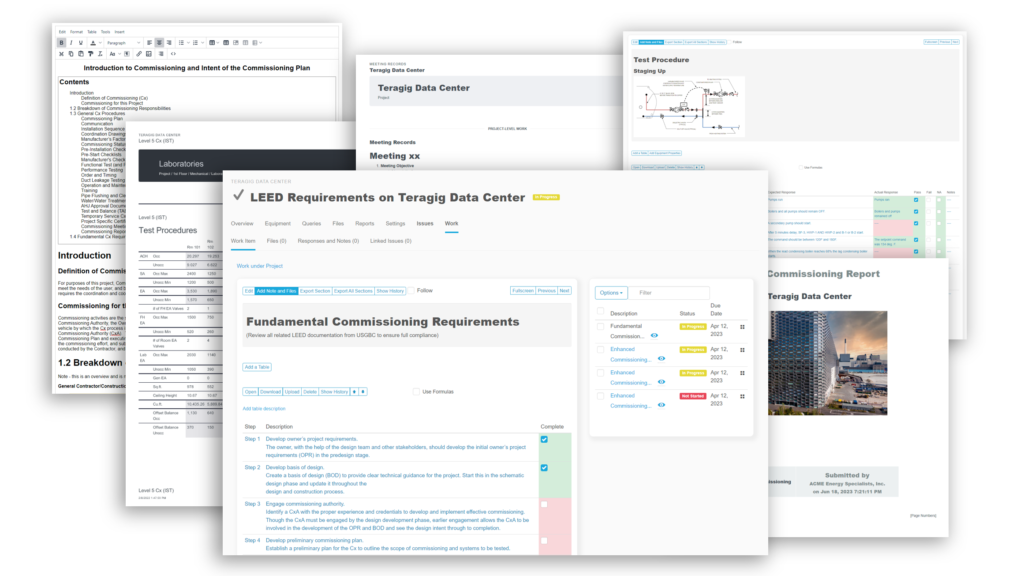
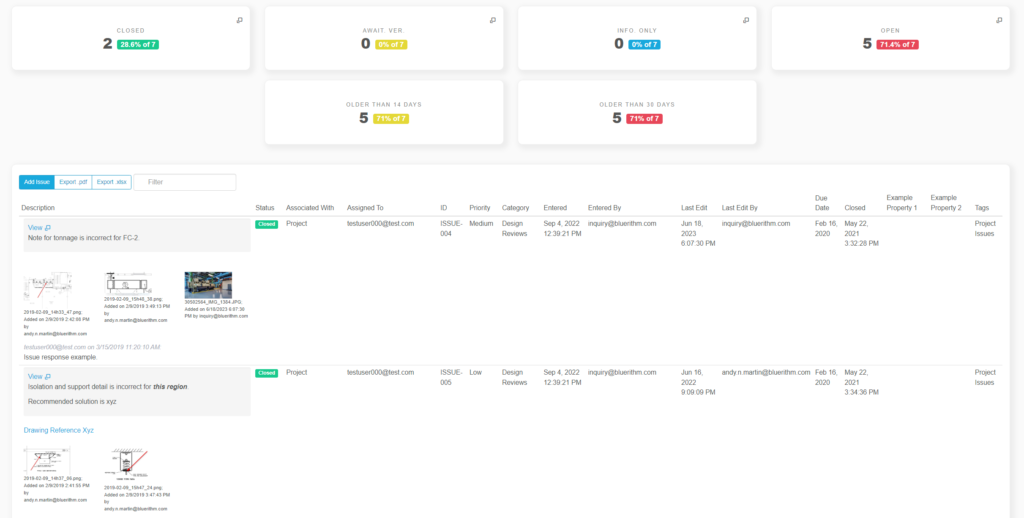
When you need a robust cloud-based platform to stay organized and ensure detail is covered for your pharmaceutical facility commissioning and qualification projects, you can trust Bluerithm to get the job done!

Guide to Pharmaceutical Facility Commissioning and Qualification
In pharmaceutical facility commissioning, “qualification” is an aspect that refers to a facility that will be operated under Good Manufacturing Practice (GMP) regulations. The first thing that should be done for pharmaceutical facility commissioning and qualification is to find out the requirements of the various regulatory authorities related to Good Manufacturing Practices, in addition to any relevant local or international laws, codes, and regulations. The European GMP for qualification and validation will apply if products are to be sold in Europe, and the Food and Drug Administration GMP (21 CFR 211.42 on building and facilities) will apply if products are to be sold in the United States.
21 CFR 211.42 includes the requirement that the pharmaceutical facility will be of suitable size and construction to both meet the goals of the facility and conform to GMP regulations. Once built, the pharmaceutical facility should accommodate proper cleaning, maintenance, and operations. Adequate space for the flow and storage of equipment and materials and support operations are important considerations.
Once general commissioning is completed, pharmaceutical facilities must be qualified and their processes validated.
Validation – the generation of documented evidence that processes are capable of consistently producing finished product that meets the quality specifications.
Table of Contents
Qualification Phases Within Validation
There are four qualification phases within the validation step. These phases include:
- Design Qualification (DQ)
- This phase outlines the roles and responsibilities of everyone on the team in developing the concept for the pharmaceutical facility and anticipates the appropriate documentation for the premises, supporting utilities, equipment, and the processes themselves. The team includes engineering and design teams, trades, subcontractors, and suppliers. Commissioning is conducted here to ensure the pharmaceutical facility is correctly designed and built.
- Installation Qualification (IQ)
- The Installation Qualification phase consists of a process to compile a documentation package that ensures receipt and proper installation of the appropriate parts and systems of the process equipment. This documentation ensures that everything is accurately installed and performing suitably and that its performance is verified per the manufacturer’s specifications. Pharmaceutical manufacturers require detailed documentation to address regulatory requirements.
- Operational Qualification (OQ)
- During this phase, the testing during commissioning is evaluated to ensure the equipment performs as specified by the manufacturer. This can be done at the supplier in some cases (Facility Acceptance Tests “FATs”) or it can be done after installation at the user (Site Acceptance Tests “SATs”). Initial phases of Operational Qualification, such as operator training, can be conducted by the equipment manufacturer oftentimes, while local site requirements related to placement, local utility supply, and local operation confirmation will be conducted in the user’s facility.
- Performance Qualification (PQ)
-
- This phase begins with a review of the Design Qualification, Installation Qualification, and Operational Qualification documentation. Data is generated and documentation is created to confirm that the installed equipment performs to the user’s requirements.
Pharmaceutical Facility Qualification
Pharmaceutical Facility Qualification is the responsibility of the end user. The facility owner needs to keep an eye on what they are delegating to the supplier. Much is expected of the supplier, including quality systems as they relate to equipment fabrication and calibration of the test equipment at the supplier, as well as any software quality assurance associated with it. The commissioning of a facility, equipment, or system for operation under GMP regulations involves qualification that all operations are suitable for the intended purpose.
Facility Acceptance Tests (FATs) and Site Acceptance Tests (SATs)
Facility Acceptance Tests are crucial to ensure the supplier and end user agree upon acceptance. The Site Acceptance Tests verify that installation was performed correctly and operating specifications are still being met.
How Handover Works for Pharmaceutical Facilities
Once the facility is handed over to the facility owner, it becomes the pharmaceutical company’s responsibility to qualify that all operations are suitable for the intended purpose because it is a regulated operation. The facility owner needs to satisfy regulators that processes are qualified and validated per GMP regulation. There must be complete documentation of all phases.
Source:
An Introduction To Pharmaceutical Facility Commissioning & Qualification
PDF Report Builder
Issue Logs and Punch Lists
Move your Excel-based processes to the cloud
Start saving time and money today