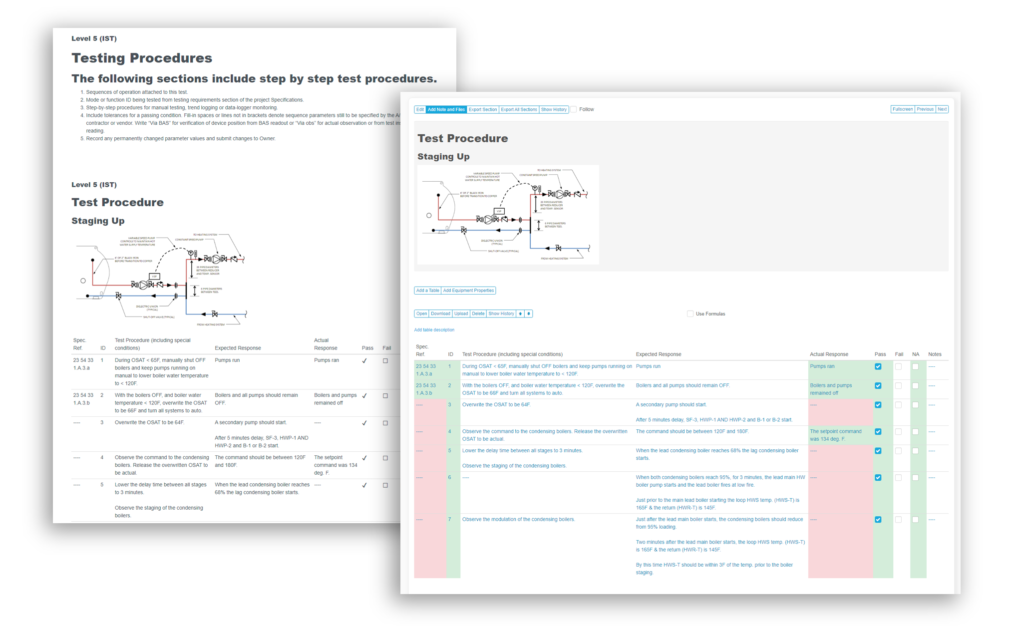
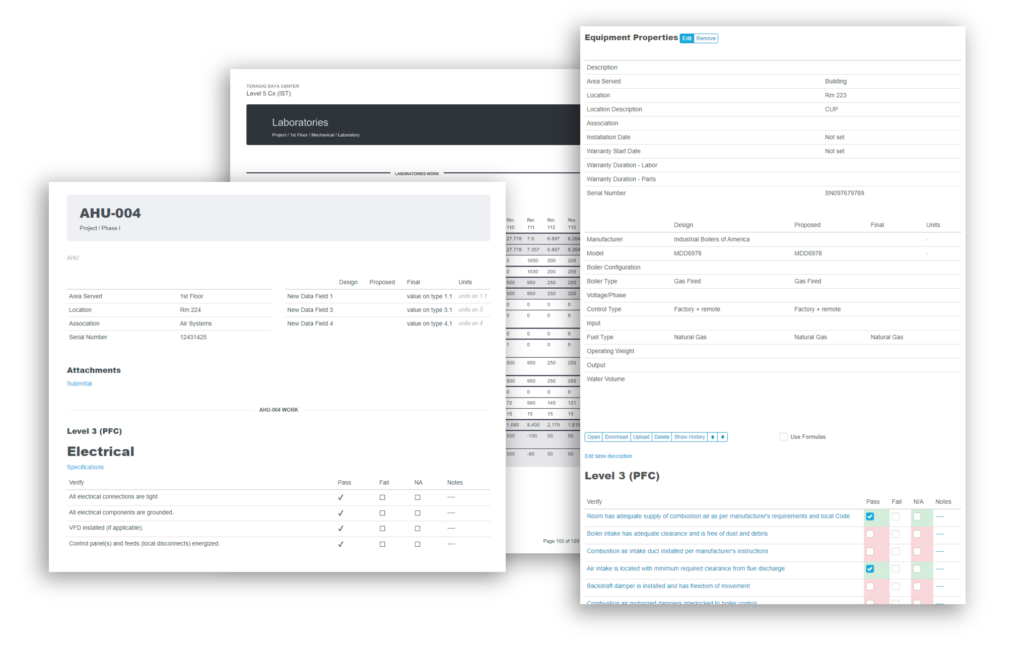
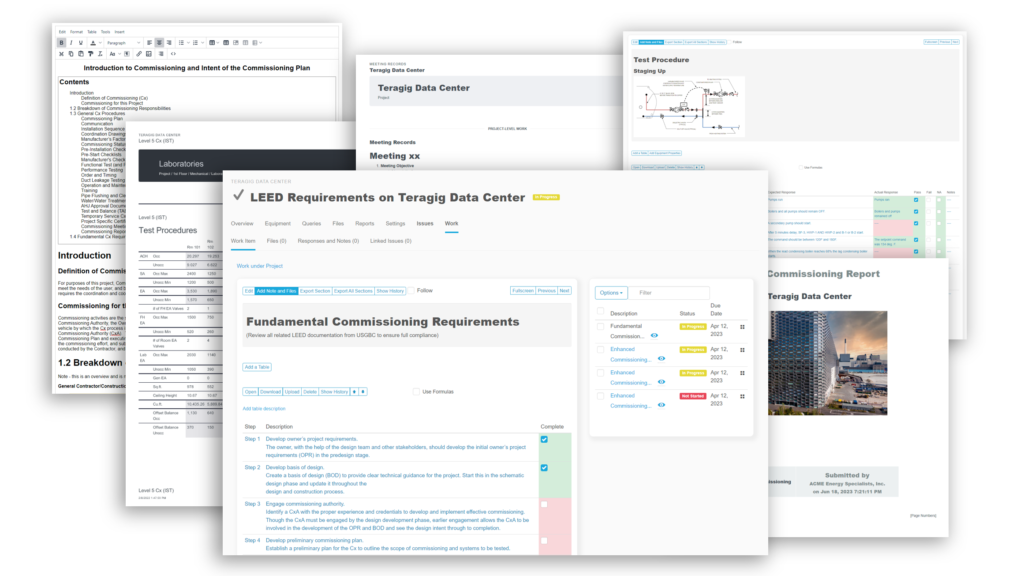
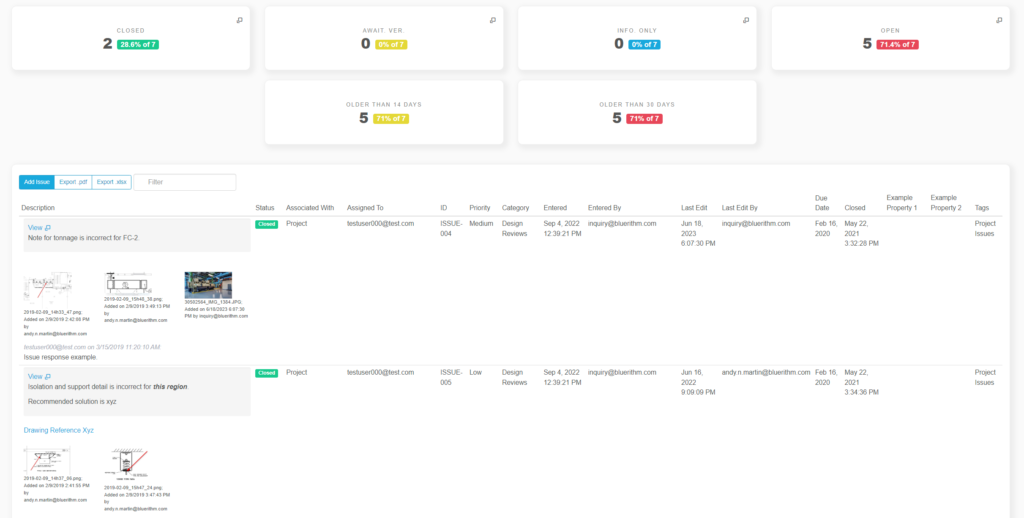
Industrial project commissioning requires a commissioning plan to be created, the proper team to be selected to carry out the commissioning activities, and detailed documentation of all commissioning tests and procedures to verify that everything was done to the correct standards and practices.
The Commissioning Plan
The commissioning plan is the project roadmap and identifies who will be involved and what their roles and responsibilities will be, and outlines the documentation that is required. Since the scope of each project differs from project to project and client to client, the team that carries out the commissioning activities also differs. It is important that the right team is assembled and is qualified to carry out the commissioning activities. At the end of industrial project commissioning, a handover package is created by the contractor and given to the owner, which includes a collection of the commissioning tests and procedures that were conducted.
Stages of Industrial Project Commissioning
There are three stages of industrial project commissioning. First, pre-commissioning occurs, which happens during the final stages of construction. The second stage is commissioning, which is sometimes called “cold” commissioning. And last comes the startup stage.
Pre-functional test (PFT) inspections, end-of-construction punch lists and check sheets, factory and site acceptance testing of control systems, and instrument loop checks are all completed during the pre-commissioning stage. The commissioning stage for industrial projects includes running and testing processes without chemicals or hazardous materials, pre-functional testing of complete building systems, pre-commissioning focusing on equipment, and commissioning focusing on the system. During the startup stage, the plant is brought into operation and the commissioning team provides engineering support as required by the owner.
We created a guide with more details related to Industrial Project Commissioning, which can be accessed here.